An understand of canonical and how to use it correctly is crucial for search engine optimization. There are many possible problems that can arise from improper implementation of canonical, and this could can have a negative effect on your site’s search engine rankings.
Webmasters have had an easier time dealing with the issue of highly similar or duplicate content accessible via different URLs since the introduction of canonical tags in 2009. However, you should know what is a canonical tag, how it functions, and how to implement it if you plan on using it.
To that end, this beginner’s guide should prove useful. Continue reading to get more details on canonical tag.
Canonical Tag vs. Canonical URL: What’s The Difference?
When a search engine encounters a canonical tag, it is instructed to only index and rank the page indicated within the canonical URL.
This is useful when you want to avoid having multiple pages with similar content flagged as duplicates by search engines.
You can find them in a page’s HTML code, specifically in the head tag. The URL it directs search engine crawlers to, can either be its own URL or another page’s URL.
The canonical URL or canonical link points to the preferred version of content for users and search engines.
Syntax Of A Canonical Tag?
The canonical tag is a simple syntax that must be inserted into the <head> section of your web page: here is how it should look:
URL: https://website.com/sample-page/?rel=canonical>
Why Is It Important To Use Canonicalization For SEO Purposes?
The use of duplicate content is frowned upon by search engines. This is because it creates issues with indexing and ranking when trying to determine which version of a page should be used. Furthermore, duplicate pages lead to cannibalization issues, wherein ‘link equity’ is divided among numerous pages that essentially contain the same information. This way, neither page benefits from a higher search engine ranking.
Having a lot of duplicate content on your website can also have a negative effect on your crawl budget. This results in search engines spending more time than necessary sifting through identical content on multiple versions of the same page.
If you don’t want search engines to waste time indexing pages that you don’t want to rank for, you should steer clear of duplicate content. However, Google claims that having duplicate content is not a problem. In most cases, a website will be efficiently crawled if it has fewer than a few thousand URLs. Canonical tags are a viable solution to problems brought on by a limited crawl budget. Use these to indicate to search engines which version of a page they should be indexing and ranking.
So, what occurs if a canonical page is not specifically added?
In the absence of a canonical URL, search engines will choose the version of your page they believe to be the most authoritative based on their own internal criteria. If they choose a variant for which you don’t want to rank, this could be a problem. Keep in mind that search engines don’t always use the canonical URL that you specify. In their case, tags are more of a suggestion than a requirement. Following established guidelines for canonical tags should reduce the possibility of unfavourable versions being marked as canonical by search engines. The pages you choose to canonicalize should ideally be related to one another.
Content Duplication
Duplicate or “similar” web pages may be created on purpose when they serve distinct functions.
Think about a scenario in which you serve clients from a variety of countries. In this case, you’ll need two nearly identical product pages with slightly different prices. These pages can be marked with canonical tags to tell search engines which version to show users based on their geographic location. In addition, there may be unseen technical factors contributing to the existence of duplicate content. Having duplicate content is a common problem for websites that are dynamic or use content management systems.
Some websites will automatically add tags that provide alternative ways to access the same content parameters (such as sorts, searches, or currency exchange rates). Because of this, it’s possible that several identical URLs will be generated for your site without your knowledge. Search engines no longer have to deal with duplicate content issues thanks to canonical URLs, which allow them to distinguish between various iterations of a page.
Problems With Multiple URLs Containing The Same Content
Duplicate content on a website can have a negative impact on search engine rankings and lead to a drop in visitor numbers. These setbacks result from two distinct problems:
The best user experience is not compromised by search engines displaying multiple versions of the same content. As a result, they pick the outcome they consider to be the best. If this occurs, your duplicates will be less noticeable.
As other websites pick and choose between the duplicates, the link equity can be diluted as well. As a result, the link equity will be distributed across multiple pages rather than just one.
Search engines also have trouble with duplicate content:
They are unsure which edition should be indexed and which should be left out.
They are unsure as to whether or not the link metrics should be aggregated on one page or distributed among several.
No one can decide how search results pages should be prioritised.
Guidelines For Writing A Canonical Tag
Canonicals are simple to put into place. Some recommendations for optimal procedures are as follows:
Using Absolute Uniform Resource Locators
When using rel=canonical, absolute paths are preferred. To avoid confusion, please do not use: link rel=”canonical” href=”/sample-page/” />
Here is a template you can follow: link rel=”canonical” href=”https://website.com/sample-page/” />
URLs In lowercase
It’s possible that search engines differentiate between URLs with and without capitalization. Canonical tags and website URLs should both be written in lowercase.
Domain Name Version Accuracy (HTTPS vs. HTTP)
You should not declare non-SSL URLs in the canonical tags if you are migrating to SSL. Doing so could cause unintended consequences and cause unnecessary confusion. If your website is hosted on a secure server, use this version of the URL: link rel=”canonical” href=”https://example.com/sample-page/” />
This is the recommended version: link rel=”canonical” href=”http://example.com/sample-page/” />
If you aren’t using HTTPS, then the inverse is true.
Use Canonical Tags That Point Back
Canonical tags that point back to themselves are known as “self-referential” tags. Although self-referential canonical tags are not required, they are highly recommended. This is so because it reveals to the search engines which pages need to be indexed. Different URLs can appear for a number of reasons, including the addition of parameters at the end or a change in case. The use of a rel canonical tag cleans everything up.
For example, if the original URL was https://example.com/sample-page, the canonical version would read: link rel=”canonical” href=”https://example.com/sample-page” />.
Some of the most widely used content management systems will incorporate a self-referential URL by default. However, a developer may be needed to do this if you’re using a custom content management system.
A Single Canonical Tag Per Page
Having multiple canonical tags on a single web page will result in all of them being disregarded by search engines.
Correctly Using The rel=canonical Tag
HTML Tag For Establishing A Canonical URL
Using the rel=canonical tag is the quickest and easiest way to designate the canonical URL. The head> section of the duplicate page can be modified by inserting the following syntax:
The canonical version of this page is located at https://example.com/canonical-page/.
If the same content appears on multiple URLs, you should use the canonical tag to indicate which URL should be used to access the content. Using a content management system (CMS) eliminates the need to modify any code.
Canonical Tag In Magento And Magento 2
Here’s what you need to do to configure Magento’s canonical URL:
In order to access the “Admin Panel,” you must first log in. Choose the “Stores” menu, then “Settings” and “Configuration,” before making any changes.
To access the Catalog, select it from the Catalog drop-down menu after clicking the Catalog option. The next step is to head on over to “Search Engine Optimization.” The subsequent adjustments are as follows:
What you can do if you want to index only those pages that belong to a specific category:
When it comes to categories, select “Yes” for the “Use Canonical Link Meta Tag” option, and select “No” when it comes to individual products.
Follow these steps to restrict indexing to just the product page:
If you want to index both products and categories, you must enable both options: Use Canonical Link Meta Tag for Categories – “No” and Use Canonical Link Meta Tag for Products – “Yes.”
Set the canonical link meta tag to “Yes” for categories and “Yes” for products.
Clearing the cache and saving your changes are required when you are finished.
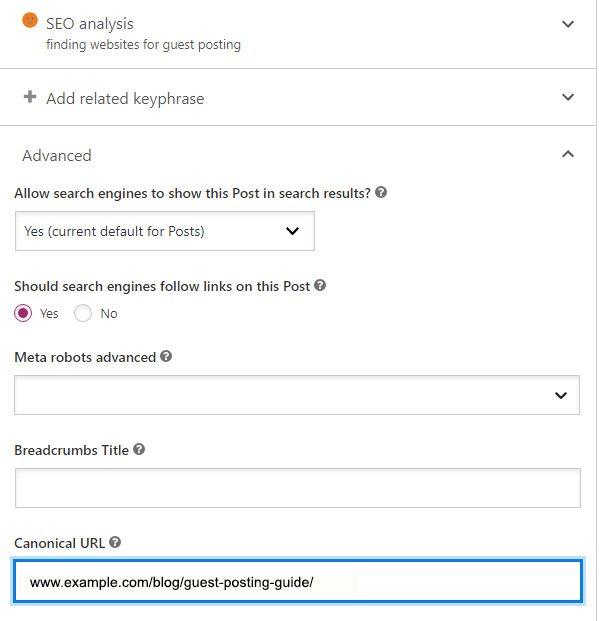
WordPress’s Canonical URL Configuration
It is necessary to install Yoast SEO in order to configure the Canonical URL in WordPress. The canonical tags for referencing themselves will be added mechanically. Custom canonicals must be set in the ‘Advanced’ section.
How To Set Your Wix Site’s Canonical URL
Whenever a new page is made on Wix, its canonical URL is generated immediately. In the Advanced SEO menu, you can modify the canonical URL or add alternative URLs that all lead to the same place.
How To Set In Shopify
If you use Shopify, your blog posts and products will have canonical URLs that point back to themselves. Changing the canonical URLs for your site is as simple as editing the template files themselves.
HTTP Header And Canonical Tag
The canonical tags cannot be inserted into the document’s head> section, as is the case with PDFs. Including the canonical code in the PHP file’s header is a simple solution.
Sitemaps With Canonical URLs
Google recommends keeping sitemaps free of non-canonical content. Only canonical URLs should be included in your list. That’s because Google will prioritise the pages included in the sitemap. There is no guarantee that canonicalization will occur for URLs that are included in sitemaps.
Sitemaps can indicate to search engines which pages you deem most important and help search engines better understand canonicals for large websites.
301 Redirects And How To Set Canonicals
A 301 redirect can be used to reroute visitors from a duplicate URL to the canonical URL. You can also switch between the “www” and “no-www” and secure and insecure “HTTP” and “HTTP” versions of the website. Find one definitive version and point all other links at it.
Use of the rel=canonical attribute at an advanced level
Now, let’s discuss some of the more advanced, specialised uses of rel=canonical:
Multiple-page Use Of The rel=canonical Tag
Because of Google’s strict adherence to the rel=canonical link parameter, it is possible to point the canonicalization of one piece of content to an entirely different piece of content. But if the search engine finds out you’ve been doing this, it may stop trusting your canonicals altogether.
Combining Hreflang And rel=canonical
When employing hreflang, it is essential that each language’s canonical link back to itself. Make sure you understand how to use canonical properly if you are implementing hreflang, or you could end up breaking it.
Mistakes in Canonicalization and How to Correct Them
4XX And Canonical Points
This alert appears when a page has been canonicalized to a 4XX URL. Search engines will not crawl these pages and will disregard any canonical tags that point to them. Due to this, it will index the incorrect version of the page. Once you have reviewed the pages, you should use the links to the active page to replace the canonical links that are no longer active.
5XX And Canonical Points
There are server problems that will make the page inaccessible, as indicated by the 5XX status codes. If you canonicalize a set of URLs, search engines will stop indexing and ignoring them. Incorrect canonical URLs must be corrected. Canonical checks for server misconfigurations if the URL appears correct. If this message appears, though, it’s likely that the server supporting your site is currently experiencing heavy traffic or is offline for routine maintenance.
Redirects And Canonicals
It’s another cause for alarm when pages are canonicalized to a 301-redirected URL. There must be a definitive version of the page for it to be included in the canonicals. The canonical will be ignored or misunderstood by search engines if a redirect URL is included.
Duplicate Pages That Do Not Have A Canonical
Without a canonical URL, search engines will use their best judgement to determine which version is most relevant to users. The page you are currently viewing may not be the one you want indexed.
Absence Of Internal Links To The Canonical URL.
If a page with one of your canonical URLs doesn’t have any internal links pointing to it, it’s considered an orphan page and won’t be indexed by search engines. They can be redirected to an alternate version of the page instead.
Sitemap With non-canonical Page
It’s possible that Google will treat non-canonical pages listed in the sitemap as suggested canonicals. If you want to fix this, you need to take these non-canonical URLs off the sitemap.
Referencing non-canonical Pages As If They Were Canonical
When a canonical URL is specified that itself is canonicalized to another page, a canonical chain is created. The results may be unclear to the search engines. A canonical link from A to B must be replaced with a canonical link from B to C, for instance.
Canonical URL For Open Graph Mismatch
This occurs when the URLs used for Open Graph and the canonical URL you provided do not match. As a result, people start spreading around a different, less official version. The canonical URL should replace the Open Graph URL, and the two should be identical.
HTTPS-to-HTTP Canonical
This happens when a secure HTTPs page designates a canonical non-secure HTTP version. A simple solution is to change the HTTP page to its secure HTTPS counterpart. If you’re unable to switch to HTTPS, you can add a ref=canonical link from the HTTP version.
HTTP to HTTPS Canonical
When an HTTPS version of a page is set as the canonical version, this warning will appear. First, set up a 301 redirect from HTTP to HTTPS, and then replace all internal HTTP links with their corresponding HTTPS counterparts.
Organic Visits To A non-canonical Page
Without the specified canonical, non-canonical pages will still appear in search results and receive organic search traffic. Make sure the rel=canonical tags are set up properly to resolve this issue. The next step is to use the URL Inspection tool to verify whether or not the canonical URL you’ve specified has been accepted.
Use Of robots.txt To Prevent Indexing Of The Canonicalized URL
The canonical tags on a page will be invisible to search engines if you block the canonicalized URL for that page in robots.txt. By doing so, you’ll stop the search engine from giving preference to the canonical URL in the event of a tie.
Putting The ‘noindex’ Meta Tag On The Canonicalized URL
Contradictory directives like rel=canonical and noindex should be avoided. It’s worth noting that Google gives the canonical tag more weight than the ‘noindex’ tag. There are two methods for making a URL canonical and noindex: 301 redirects and rel=canonical.
Canonical Tags: How To Conduct An Audit
Many factors affect how well your canonical tags perform for search engine optimization, so it’s important to check them all during an audit.
- Presence or absence of canonical tag for a given page.
- Is the correct page referenced by the canonical tag, if present?
- Do search engine spiders and indices have access to this page?
You can verify the validity of the canonical tags in the following ways:
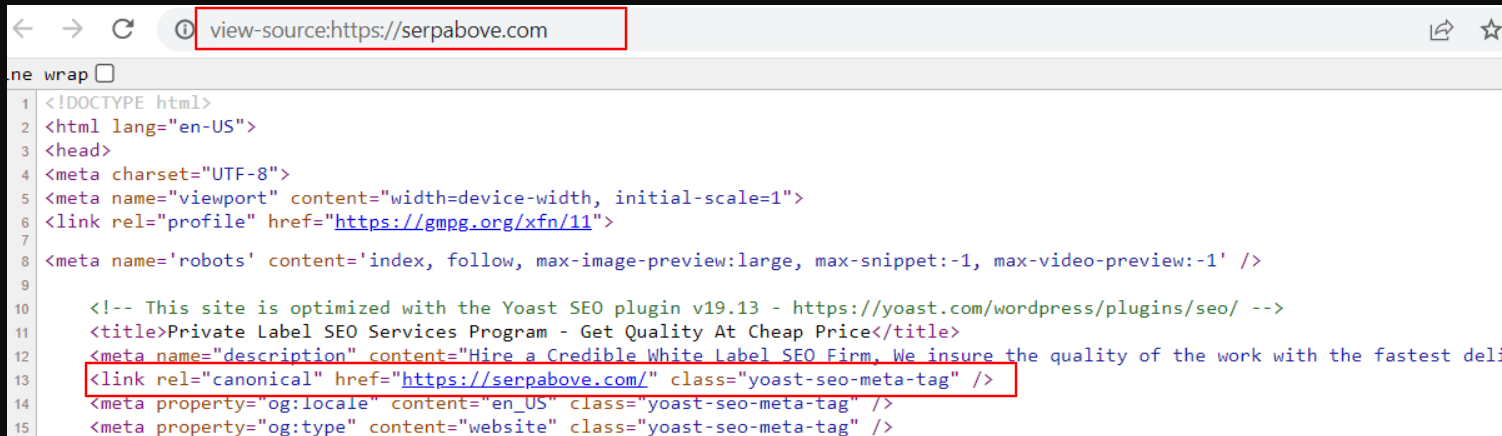
View-Source
Right-clicking the browser and selecting “view-source” will allow you to inspect the code behind the page. Enter view-source: in the address bar to see the source code (address of the page).
Search Engine Optimisation Software options
Several search engine optimization (SEO) tools are available online and can help you perform a bulk audit of canonical tags.
Canonicalization has been cited as an essential SEO concept. Your website won’t perform as well as it could if it wasn’t properly implemented. In any case, once you learn what a canonical URL is, what a canonical tag is, what they do, and how to resolve canonicalization issues, you’ll be able to use them effectively and eliminate duplicate content from your site.